 Кирюба Мария Сергеевна,
Кирюба Мария Сергеевна,
ОмГУ им. Достоевского г. Омск
In the modern economy an increasing critics of GDP becomes the main indicator of the development. The looking for a new universal indicator that takes into account all aspects of society turns out the topical problem of economics. Against this background a new theory began to form. And such an exact characteristics of the happiness comes in.
Economic growth is intended to be a means to the end of social well-being. However, as society focuses on what is being measured, the means become the end. In other words, Western nations make the mistake of equating economic growth to social well-being [3].
Life is better now than at almost any time in history. More people are richer and fewer people live in dire poverty The world is hugely unequal. Today the most widely used measure of poverty is most widely used, along with a national poverty line or an international standard [4].
The term wellbeing refers to all of the things that are good for a person, that make for a good life. Wellbeing includes material wellbeing, such as income and wealth; physical and psychological wellbeing, represented by health and happiness; and education and the ability to participate in civil society through democracy and the rule of low [1].
The income and the growth remain vital. Income is critical in determining people’s command over the resources necessary to gain access to food, shelter and clothing. it is also the source of the taxes and other revenues that governments need in order to provide services and undertake redistributive programs. Thus, increasing income on a broad basis remains an important policy priority [4].
There is an opinion that too much attention is given to income. More over money does nothing to make people’s lives better; at least once basis needs to have been met [1].
It is impossible to agree with this point of view because people are the real wealth of the nation [4]. Based on this, it can be argued that the measure of the social wellbeing cannot be reduced to one quantitative number, Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a period (quarterly or yearly).
So a simple index, The Human Development Index (HDI), was devised explicitly as a rival to GNP and concentrating only on longevity, basic education and minimal income. It works as a simple measure like GNP without being oblivious of anything other than incomes and commodities [4].
Disadvantages of GDP were studied in many countries. But the small Kingdom of Bhutan has been trying to understand one innovative idea. In 1972, concerned about the problems afflicting other developing countries that focused only on economic growth, Bhutan’s King decided to make his nation’s priority not its GDP, but GNH or gross national happiness [5].
Economic theory of happiness is a new direction, which considers the subject-representations of the person about their live satisfaction as an economic phenomenon, happiness factors, his dependence on the level of economic development of the country.
GNH Index assesses the effectiveness of the state based on the level of happiness of its citizens. Key indicators of GNH: health, education, active public and social life, preservation of ecological diversity and stability, good governance, security.
According to a survey VCIOM on April 18, 2016 majority of Russians
(83%) feel that they are in general happy people: the happiness index is 68 [6].
If we compare the level of happiness of the country and the level of GDP, most "happy" countries are not the rich, and the rich are not always happy. The level of HDI supports this trend [7].
|
Place in the ranking |
Country |
GDP per capita |
HDI |
GNH |
|
1 |
Denmark |
13018 |
0,923 |
7,526 |
|
2 |
Switzerland |
15681 |
0,93 |
7,509 |
|
3 |
Iceland |
14175 |
0,899 |
7,501 |
|
4 |
Norway |
19243 |
0,944 |
7,498 |
|
5 |
Finland |
12423 |
0,883 |
7,413 |
|
6 |
Canada |
15083 |
0,913 |
7,404 |
|
7 |
Netherlands |
14306 |
0,922 |
7,339 |
|
8 |
New Zealand |
10845 |
0,913 |
7,334 |
|
9 |
Australia |
15042 |
0,935 |
7,313 |
|
10 |
Sweden |
14380 |
0,907 |
7,267 |
|
56 |
Russia |
6477 |
0,793 |
5,8 |
|
154 |
Afghanistan |
413 |
0,465 |
3,5 |
|
155 |
Togo |
900 |
0,484 |
3,3 |
|
156 |
Syria |
0 |
0,594 |
3 |
|
157 |
Burundi |
197 |
0,4 |
2,9 |
The level of material wellbeing is not decisive. It's confirmed by the results of the sociological survey, which was conducted among 17-25-years-old young of Omsk. 61 individuals were interviewed ( the results on the diagrams).
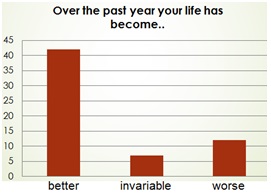
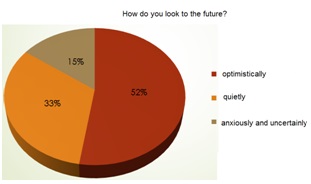
The main attention was paid to the criteria of safe happy life. The following items were suggested as an alternative: have a family, love and to be loved, be healthy, be financially secure, be independent, take care of others, feel safe.
The findings: the material side of happiness occupies only the fourth position out of ten. Young give preference to emotional and physical well-being, but the revenue as the happiness factor is not excluded.
In the opinion Amartya Sen the psychological happiness is just one of components of the general welfare. Economist concluded that it is important not so much made of GDP, and there are all the public access to works.
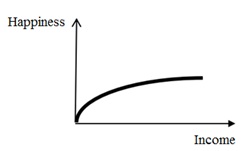 |
Happiness is in the money if on them to achieve basic physiological needs (Maslow's theory). Therefore, happiness is the limit function of income, and we can calculate the point from which, with a further increase in income the level of happiness does not increase, and even decreases.
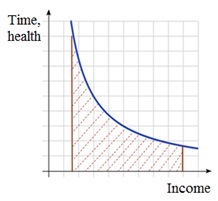 |
There comes a time when an individual can no longer be neglected for the benefit of others benefits. Thus, we can reduce the problem of determining the level of happiness to the tradition economic analysis of "cost-benefit» and it's really as follows: working for profit, the person reduces the amount of free time, health. It can be presented as the level of happiness figures the area under timetable as the limiting value.
The world today is moving towards recognition of the priority socio-economic values are more important than the value of only the material wellbeing, i.e. criteria of the wellbeing from the perspective of values and the identity.
GNH as an indicator, which considers additional criteria happiness, must be considered along with the GDP.
Happiness Economics promotes the positive development of both macro-economic wellbeing and improves the living standards of the individual.
Also human development index was developed and scientifically proved as the generalized system of indicators characterizing the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the social and the economic differentiation of the social development.
It was found that the economic growth is not automatic the life satisfaction based on the scientific evidence and my own research. Therefore, the level of the happiness and the human development necessary to complete the assessment of the people’s wellbeing.
Of course, we can not provide the happiness to all people. But the goal of the economy is to create the conditions in which it is possible to ensure life satisfaction. Economics of happiness will change for the better, not only the global economy but also the lives of each individual.
References
- Angus Deaton “The great escape: health, wealth, and the origins of inequality” (copyright © 2013 by Princeton University Press, Nobel Prize in Economics 2015).
- Daniel Kahneman and Angus Deaton “High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional wellbeing”, 2010.
- Frank Dixon “Gross National Happiness: Improving Unsustainable Western Economic Systems”, 2010.
- Jeni Klugman “The real wealth of nations: pathways to human development”.
- Andrew C. Revkin “A new measure of Wellbeing from a happy little Kingdom”
- URL: http://www.wciom.ru
- URL: http://worldhappiness.report/
